복부 CT를 판독하는 것은 처음에는 매우 부담스러운 일입니다. 이 글은 복부 CT를 판독하는 순서에 대해서 정리해 보겠습니다.
이 글은 Navigating radiology라는 youtube 채널의 영상 내용을 참고했습니다.
Reference)
https://youtu.be/Nnr4ZB8e4nc?si=PnZiuFxklX0xfvu7
https://radiologyassistant.nl/
https://radiopaedia.org/cases/how-to-read-a-ct-of-the-abdomen-and-pelvis
Disclaimer) 이 글은 복습용으로 쓰여졌으며 진단 또는 치료의 목적으로 사용되어서는 안됩니다.
Lower chest
- Lung bases
- Pleural effusion
- Pericardial effusion
Liver


- Hepatic artery: CT와 angiography의 이미지를 머릿속에서 합칠 수 있는 능력이 있어야 합니다.

Hepatic artry angiography. Case courtesy of Associate Professor Donna D'Souza, Radiopaedia.org. From the case rID: 36182
- Ligaments
- Ligamentum teres: 간의 좌엽을 medial, lateral portion으로 나누는 구조물입니다. 이것은 segment 4a와 3을 구분하는데 유용하게 쓰입니다.
- Ligamentum venosum: 간의 segment 2와 1 (caudate lobe)을 구분하는 지표입니다. CT에서 ligamentum venosum을 지나가는 artery가 보인다면 그것은 anatomic variant입니다. 주로 SMA에서 분지 하는 left hepatic artery의 variant가 ligamentum venosum을 지나갑니다.
- Fossa for ductus venosus = ligamentum venosum, Round ligament = ligamentum teres
- Focal fat: 간의 일부분에 focal fat sparing 또는 fat deposition이 생기는 경우가 있습니다. Falciform ligament, S4, GB fossa, S2가 대표적인 fat sparing이 나타나는 장소이고, 이곳에 fat deposition이 보인다고 해서 임상적으로 큰 의미는 없습니다.
Gall bladder, biliary tree
- GB
우선 GB가 있는지 확인합니다. GB가 있다면 GB wall thickness를 확인해야 합니다. 만약 focal wall thickeness가 있다면 GB cancer가 아닌지 의심해야 합니다. 정상 GB wall은 3mm 미만입니다. GB distension 있는지, GB 내 low 또는 high density stone이 보이는지 확인합니다 - Intrahepatic bile duct
IHD dilatation은 주위 portal vein과의 비교를 통해서 판단합니다. Right hepatic duct와 left hepatic duct는 5 mm 이상이면 dilatation이 있다고 말합니다. 통계적으로 portal vein의 diameter의 25% 이상의 크기라면 dilatation이 있다고 말합니다. - CBD
6mm 미만이 정상입니다. Bile duct의 diameter는 가장 proximal 한 위치, 간과 연결되는 곳에서 측정합니다. Proximal portion에서 common bile duct와 right hepatic artery가 교차할 수 있기에 그 artery의 직경을 제외하고 측정합니다. CBD는
Pancreas
Pancreas는 retroperitoneal organ이며, anterior pararenal compartment에 존재합니다. Uncinate process, head, neck, body and tail으로 구분됩니다.
Head: Superior mesenteric vessel(SMA, SMV)의 오른쪽
Uncinate process: Superior mesenteric vesse의 뒤쪽
Neck: thinnest part, SMA, SMV의 앞쪽
Body: SMA, SMV의 왼쪽
Tail: 유일한 intraperitoneal part
- Morphology
- Enhancement
- Lesions
- Ductal dilatation/anatomy:
Main pancreatic duct가 dilatation이 있는지 확인합니다. 일반적으로 head에서는 3mm 미만, body에서는 5mm 미만이 정상입니다. Main pancreatic duct의 직경이 7mm 이상 커졌을 때 worrisome feature가 있다고 말하고, 10mm 이상이라면 high risk stigmata가 있다고 말합니다 - Splenic vein: 일반적으로 straight 하며 pancreas neck의 posterior 부분에서 superior mesenteric vein과 만나서 portal vein을 이룹니다.
- Splenic artery: undulating course를 보이며, calcification이 흔하므로 pancreatic calcification과 혼동될 수 있습니다.
Spleen
- Size: largest diamter가 12 cm을 넘으면 splenomegaly가 있다고 말합니다.
- Enhancement
특징적으로 arterial phase에 serpentine, zebra pattern을 보이는데 이것은 spleen 안의 red pulp와 white pulp의 조영증강 속도의 차이 때문입니다. 이것은 정상적인 소견이며, 특히 liver protocol CT를 찍을 때 arterial phase가 정확한 time interval을 두고 찍혔는지 판단하는데 도움이 됩니다. - Masses
Adrenal gland
- Morphology: Y 또는 V 모양입니다. limb thickness < 1 cm 미만이어야 하고, concave 한 모양을 가져야 합니다.
즉, 두께가 1 cm 이 넘거나, convex margin을 가진 adrenal gland는 비정상입니다.
일반적인 density는 muscle density입니다. - Masses
Kidney, ureter and bladder
- Normal size: 9 - 13 cm
- Morphology
- Enhancement: Symmetric
- Masses: 특히 RCC는 hypervasular mass로, kidney parenchyme과 구분하기 쉽지 않으므로 symmetry 및 axial과 coronal image를 비교하는 습관을 들입시다.
- Stones
- Collecting system
- Ureters
- Bladder: distension, wall thickness, luminal contents. Pelvic trauma 환자에서는 CT cystography를 통해서 bladder rupture의 종류를 감별하는 것이 치료방향을 결정하는데 중요합니다
- Intraperitoneal rupture: CT cystography상 foley catheter를 통해 주입한 contrast가 paracolic gutter 등 bowel 주위 공간으로 퍼질 때는 말합니다. 이것은 bladder dome 등이 터져서 intraperitoneal rupture가 생겼음을 말하고, 수술적인 치료가 필요합니다.
- Extraperitoneal rupture: CT cystoscopy를 통해 foley catheter로 넣은 contrast가 bladder 밖의 extraperitoneal space에만 있다면 곧바로 수술을 할 필요는 없습니다. Conservative treatment를 먼저 합니다.
Bowel
- Esophagus:
normal wall thickness < 3 mm. Esophagus에서 가장 흔한 subepithelial tumor는 leiomyoma입니다. - Stomach:
Fundus, body, antrum, medial and lateral curvature. normal wall thickness < 5 mm. - Duodenum: 4개의 portion으로 나뉩니다.
1st portion: duodenal bulb라고도 불립니다. 다른 부위에 비해서 dilation 되어 있습니다.
2nd portion: pancreas head level입니다. Common bile duct와 pancreatic duct가 major duodenal papilla(ampulla of Vater)를 통해 통과합니다.
3rd portion: superior mesenteric artery가 앞쪽으로 지나갑니다.
4th portion - Jejunum: left, ileum: right
- Terminal ileum:이 부위에 bowel wall thickening이 있다면 crohn's disease 나 becet's disease 등을 의심할 수 있습니다.
- Ileocecal valve: Intussusception이 의심되는 환자는 이 부위를 잘 관찰해야 합니다.
- Colon & rectum: cecum, ascending colon - hepatic flexure까지 가고 transverse colon은 splenic flexure까지 갑니다. Descending colon, sigmoid, rectum 순으로 이어집니다.
- Appendix:
찾는 방법: IC valve를 찾습니다. → Appendix는 terminal ileum과 같은 side에서 나옵니다. → IC valve에서부터 cecum을 따라 proximal 하게 장을 따라서 스크롤하다 보면 appendix를 확인할 수 있습니다.
Normal diameter < 6mm. Appendix의 직경이 6mm를 넘거나, periappendiceal fat-stranding이 있거나, fecolith가 있을 때 appendicitis를 의심할 수 있습니다. - Bowel wall thickening:
Normal <3mm.
oral contrast medium으로 bowel을 distension 시켜야 정확한 판단이 가능합니다.
Mild: 3- 5 mm, Moderate: 5 - 9 mm, Severe: >= 10 mm
Normal bowel wall과 pathologic bowel wall thickening을 구분해야 합니다. 쉽지 않지만, 좋은 방법은 반대편의 정상적인 bowel과 비교를 하는 것과 정상적인 bowel wall layer가 유지되어 있는지 확인하는 것이 중요합니다. - Bowel distension: 3-6-9 rule:
Small bowel은 3, large bowel은 6, cecum 은 9 cm 보다 크면 distension이 있다고 말합니다.
중요한 것은 small bowel의 closed loop처럼, afferent loop과 efferent loop을 비교하는 것입니다. - Hernias (ventral, umbilical, spigellian, parastomal, lumbar, inguinal, femoral, obturator, sciatic)
- Fluid collections
- Free fluid
- Free air
- Peritoneal or omental implants
Peritoneum
Peritoneum, mesentery, peritoneal space에 대해 알아보겠습니다.
- Peritoneum: 복강 내 장기를 둘러싸고 있는 얇은 막입니다.
- Parietal peritoneum은 복벽을 둘러싸고 있고
- Visceral peritoneum은 장기를 둘러싸고 있습니다.
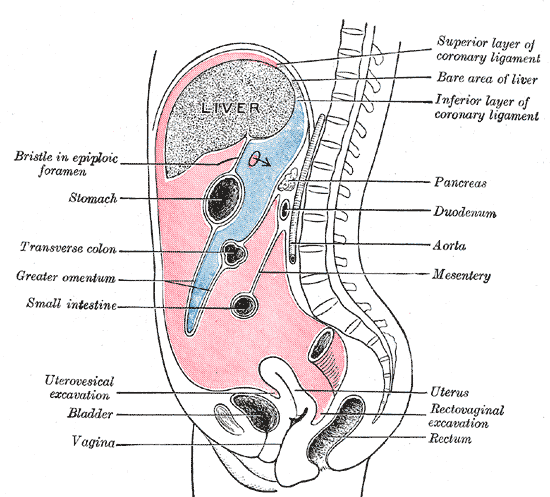
- Mesentery:Mesentery는 peritoneum 2 개의 layer로 이루어진 구조를 말합니다.
- True mesentery: posterior peritoneal wall에 붙어있고, small bowel mesentery, transverse mesocolon, sigmoid mesentery가 있습니다.
- Specialized mesentery: bowel과 bowel 사이를 연결하고 greater omentum, lesser omentum, mesoappendix가 있습니다.
- Peritoneal space
- Right subphrenic space: Morison pouch는 환자가 누웠을 때 fluid, blood가 고여 있을 수 있는 공간입니다.
- Left subphrenic space: right subphrenic space와 falciform ligament로 분리되어 있습니다.
- Lesser sac: stomach과 pancreas 사이의 독립된 peritoneal space입니다.
- Greater sac: lesser sac을 제외한 나머지 peritoneal space를 말합니다. Lesser sac과는 foramen of Winslow로 연결되어 있습니다.
- Paracolic gutter: Ascending colon과 descending colon 옆의 공간을 말합니다.
- Pelvis에는 blood, fluid가 모두 고이게 되는데 이것은 pelvis가 가장 낮은 공간이기 때문입니다. 따라서 Duglas pouch, rectovesical space, vesicorectal space 등은 ascites가 있는지 확인하기 위해서 가장 먼저 보아야 할 공간입니다.
Vessels
- Abdominal aorta
- Visceral arteries:
- Celiac
- Common hepatic
- Splenic
- Left gastric
- Renal
- SMA:
Superior mesenteric artery는 T12 - L1 level에 있습니다. 이것은 angiography를 하기 위해서 catheter를 위치시킬 때 중요한 anatomic landmark입니다. 앞서 잠깐 언급한 것처럼, portocaval space와 ligamentum venosum에 artery가 보인다면, variant입니다. - IMA
- Iliac, pelvic and femoral arteries and veins
- Vein: 내부에 low density를 가진 thrombus가 있는지 확인하는 것이 중요합니다.
- SVC
- Portal vein
- IVC
- Common iliac
- Femoral
- Popliteal
Lymph nodes
- Lower chest
- Upper abdomen (gastrohepatic ligament, celiac, portocaval, porta hepatis <periportal>)
- Retroperitoneum
- Paraaortic nodes: aorta 주위
- Aortocaval nodes: aorta와 IVC 사이
- Retrocaval nodes: IVC의 뒤
- Precaval nodes: IVC의 앞
- Common, external, internal iliac nodes: artery의 주위
- Mesorectal nodes: rectum 주위 - colon, rectal cancer 있으면 주의 깊게 관찰
- Superior rectal nodes: rectum의 위
- Pelvic side walls
- Inguinal nodes
- Mesenteric nodes: mesentery 안에서 vessels은 tubular structure라서 서로 연결이 되지만, nodes는 연결되지 않는다는 점에서 구분할 수 있습니다.
Retroperitoneum
Retroperitoneum은 parietal peritoneum과 abdominal wall 사이의 공간을 말하며, anterior pararenal space, perirenal space, posterior pararenal space 3개로 나뉩니다.
- 흔히 SAD PUCKER로 retroperitoneal organ을 외우기도 합니다.
- Suprarenal (adrenal) glands
- Aorta and IVC
- Duodenum (2nd through 4th parts)
- Pancreas (except tail)
- Ureters
- Colon (descending and ascending)
- Kidneys
- Esophagus (thoracic portion)
- Rectum (partially)
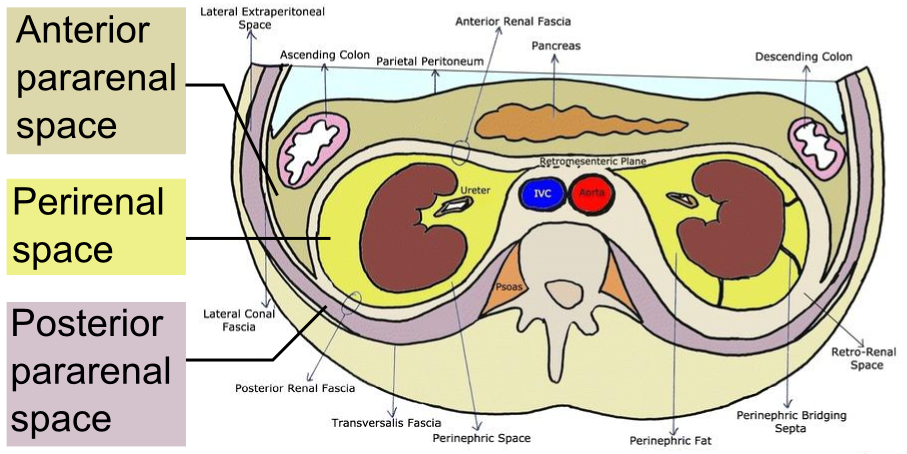
- Anterior pararenal space: duodenum, ascending, descending colon, pancreas 등이 있는 공간입니다. acute pancreatitis 등으로 인해서 생긴 염증이 이동하는 공간이 되곤 합니다.
- Perirenal space: kidney, adrenal gland, ureter 가 있는 공간입니다. 위쪽으로 liver의 bare area와 연결되어 있습니다.
- Posterior pararenal space: fat 외에는 아무것도 없는 공간입니다.
Pelvic organs
- Uterus: size, position, endometrium, masses.
- Fallopian tubes
- Ovaries: Pelvis에 보이는 병변이 ovary에서 origin인지 확인이 어려울 경우에는 ovarian vein을 tracing에서 연결되는지 확인합니다.
- Cervix
- Vagina
- Prostate and seminal vesicles: size, contour, definition, calcifications
- Spermatic cord
- Imaged scrotum and penis
Musculoskeletal
- Aggressive lesions
- Benign lesions
- Fractures
- Vertebral body heights
- Degenerative disease
- Musculature and subcutaneous tissues
'Columns' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Brain MRI: Loss of consciousness (thalamus anatomy) (0) | 2024.05.03 |
|---|---|
| Case study: Pontine infarction (0) | 2024.04.30 |
| 책 정리를 하지 않았다면 공부를 하지 않은 것과 같다 - 이윤규변호사 책 정리법 (0) | 2024.03.13 |
| 의대 증원 사태, 그리고 한국 의료의 문제 (5) | 2024.02.24 |
| 영상의학과 의사란 무엇인가? (2) | 2023.10.01 |



